What is Factory Pattern?
The factory design pattern is a creational pattern that provides a way to create objects without specifying the exact class of the object that will be created. This is useful when the process of creating an object is complex or you want to abstract the object creation process from the rest of the application.
Example:
class Dog:
def __init__(self, name):
self._name = name
def speak(self):
return "Woof!"
class Cat:
def __init__(self, name):
self._name = name
def speak(self):
return "Meow!"
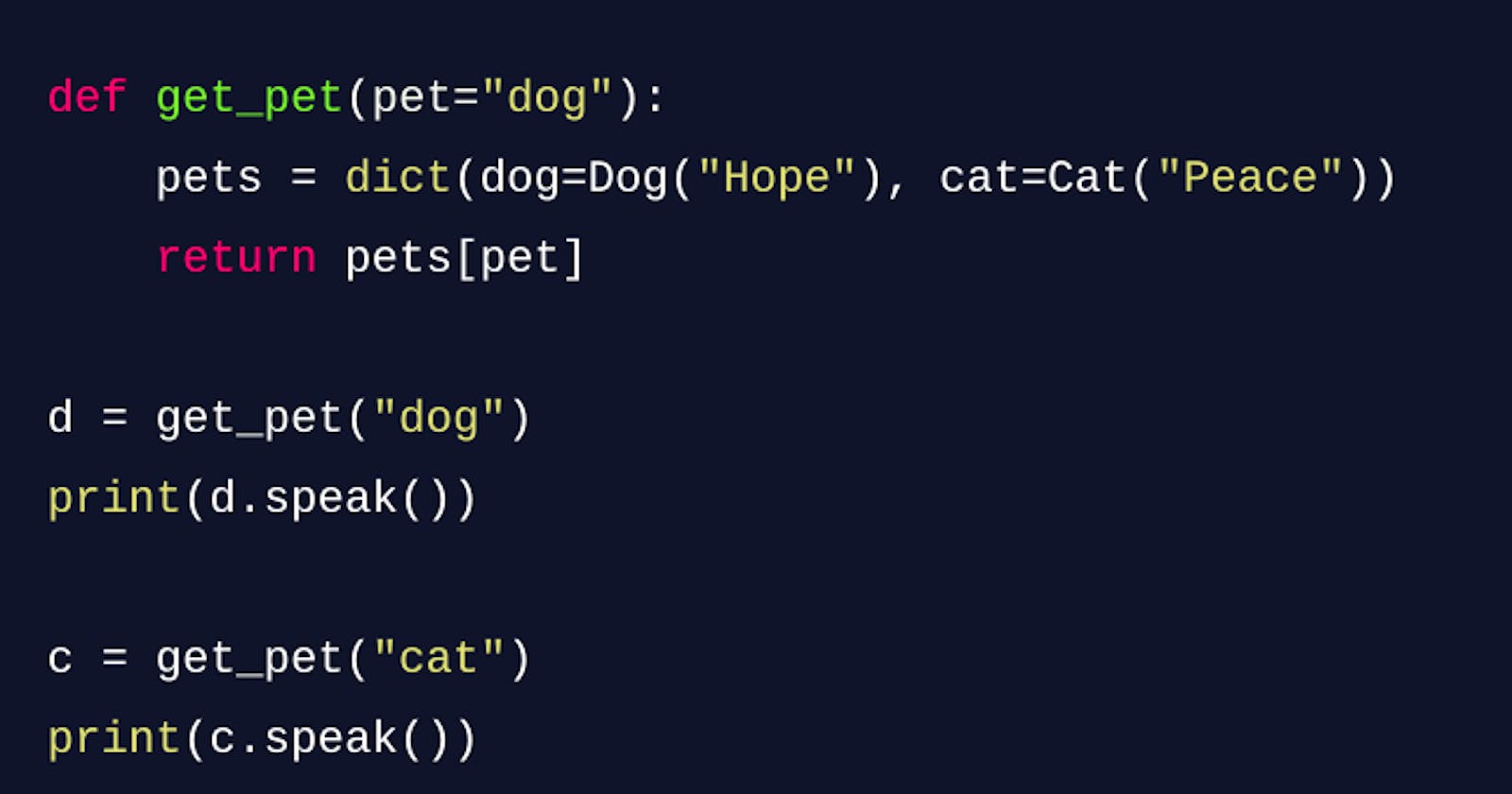
def get_pet(pet="dog"):
pets = dict(dog=Dog("Hope"), cat=Cat("Peace"))
return pets[pet]
d = get_pet("dog")
print(d.speak())
c = get_pet("cat")
print(c.speak())
In this example, we have two classes Dog and Cat each with their own speak method. The get_pet function acts as a factory that takes a string pet as a parameter and returns an instance of either the Dog or Cat class, depending on the value of the pet parameter. The factory function uses a dictionary pets to map the string values to the respective classes.
By using the factory pattern, the rest of the application does not need to know about the specific classes that are being created, it only needs to know about the get_pet function and the speak method, which provides a clean and abstract interface for creating objects.